Ty Robinson | February 6, 2025 | Personal Injury
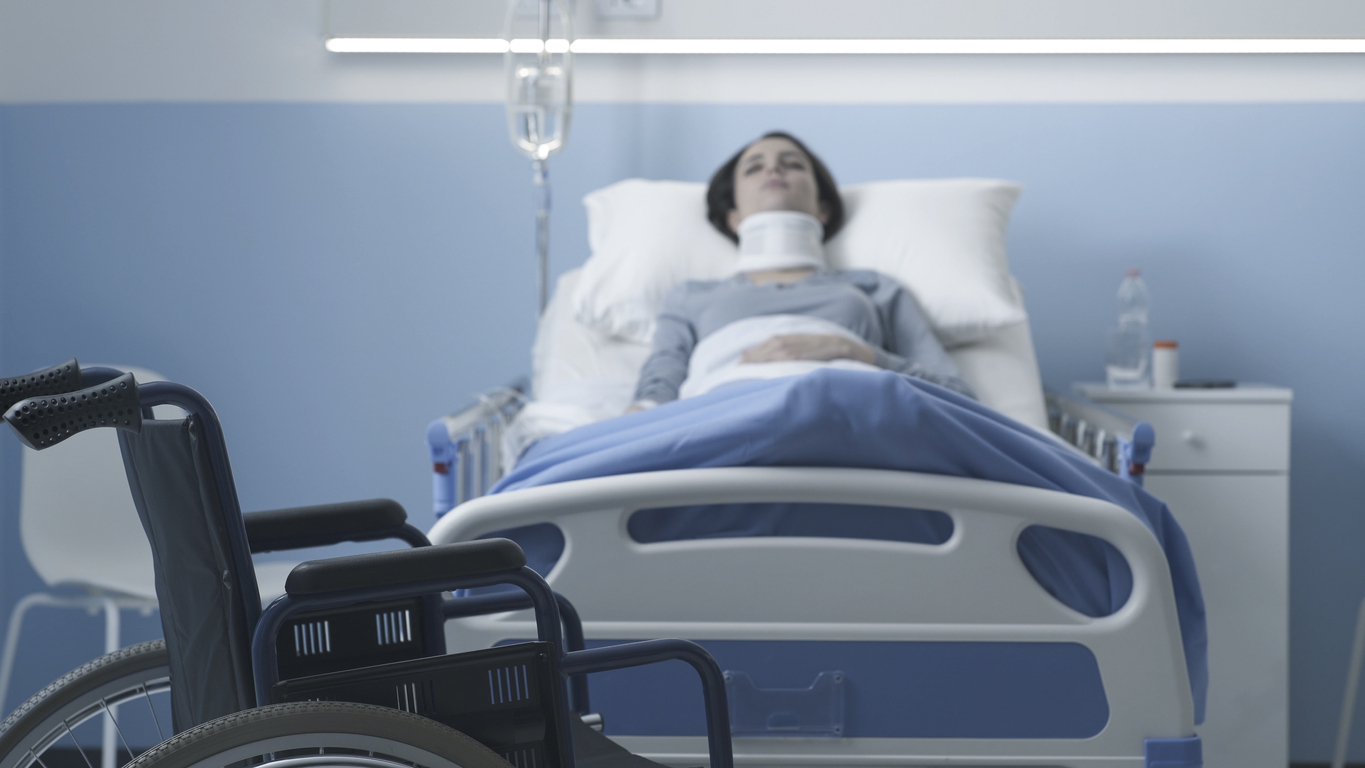

Concussions can be associated with high-risk activities like skiing or tackle football. But concussions can also occur in other common activities we enjoy or in events such as car accidents. No matter how a concussion happens or whether you feel alright afterward, concussions should be taken seriously and not left untreated.
Failure to treat a concussion could lead to permanent damage or even death. If you have suffered a concussion because of someone’s negligence, it is advisable to contact a brain injury lawyer right away.
What Is a Concussion?
There is some medical uncertainty about what a concussion is. However, most healthcare practitioners agree that it is a type of traumatic brain injury, abbreviated “TBI.”
The Centers for Disease Control states that a concussion is “caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head” or by a “hit to the body that causes the head and brain to move rapidly back and forth.” This kind of direct and abrupt contact with the head can cause quick, jostling movements, rapid enough to make the brain jolt around inside the skull. The brain might also twist around, resulting in damage to brain cells.
Danger of Repeated Concussions
While even one concussion should not be taken lightly, there is an increase in the chance of lasting effects on your health if you sustain more than one concussion. This is especially true if the second concussion happens before you have a chance to heal from the first. It is more damaging if you engage in activities that put you at risk for multiple, repeated concussions.
Repeated traumatic brain injuries cause death to nerve cells in the brain. Death to nerve cells can result in cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and behavioral problems.
Common Activities Associated with Concussions
It is hard to imagine every scenario in which a concussion could occur.
Here are a few activities and events that may increase your risk for a concussion:
- Collision between athletes in high-contact sports, such as American football or soccer
- Motor-vehicle accidents
- For youth, falls from playground equipment
- Assault to the head for sport, such as in boxing and mixed martial arts
- A fall from a great height or from a bicycle, scooter, or roller skates onto a hard surface
- Extreme sports are characterized by high speeds and rapid movements, such as skateboarding, skiing and snowboarding
- Intentional criminal assault and abuse
Concussions can happen to anyone in an array of activities.
Immediate Symptoms After a Concussion
Some people may experience immediate symptoms after a concussion. These symptoms often include headaches, blurred vision, dizziness, eye strain, light sensitivity, brain fog, and confusion. These symptoms are signs that you should seek medical attention right away.
Even if you do not experience extreme pain or see bleeding, it is vital that you do not mistake a lack of pain for lack of injury. Even a minor concussion is still a traumatic brain injury. Some may feel the need to dismiss the concussion or shake it off, so to speak. That would not be wise.
Left untreated without proper medical care leaves you vulnerable to reinjury if you’re not careful. This is especially true for athletes who want to keep playing and get back in the game. Medical practitioners can also alert you about delayed symptoms to watch for that you might not otherwise connect with an earlier concussion.
Delayed Concussion Symptoms
If you do not experience immediate symptoms after a concussion, it is important to be vigilant about symptoms that may arise later. Some symptoms are now known to persist for a longer duration or not appear at all until years or decades after the initial injury occurred. Here is what you can look out for:
Persistent post-concussive symptoms
Post-concussion syndrome (PCS) is when you have concussion symptoms continuing after your initial concussion. While most concussion symptoms end within two to six weeks, a PCS diagnosis is likely when symptoms persevere beyond that time. You might not notice these symptoms at first, and because of that, it’s advisable to remain aware of how your body feels and take note if you aren’t feeling like yourself.
Symptoms of post-concussion syndrome include:
- Headaches or migraines
- Tiredness
- Irritability
- Anxiety and/or depression
- Insomnia, such as trouble falling asleep or sleeping too much
- Inability to focus; poor concentration and memory
- Ringing in the ears
- Vision problems
- Sensitivity to light and noise
- Nausea or vomiting
- Neck pain
Currently, medical practitioners do not know why some people develop persistent post-concussive symptoms. Some doctors believe that such symptoms are caused by several risk factors, including past head injuries, other brain-related conditions like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), or a history of behavioral health conditions.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy or CTE
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive and fatal brain disease associated with repeated traumatic brain injuries, including concussions and repeated blows to the head. Media recognition of high-profile American football players who have experienced repeated concussions has drawn the attention of the public to research CTE. The research shows that repeated head trauma can leave people at high risk of developing what is known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy or CTE. This is a severe brain disease that results from continual jarring to the head.
Those who experience CTE are diagnosed through symptoms that may not occur until years, sometimes decades, after the head trauma first occurs.
The symptoms related to CTE include:
- Loss of memory and confusion
- Behavioral changes that include depression and increased suicidal thoughts
- Signs of aggression
- Lack of impulse control
- Inability to focus and lack of mental clarity.
- Symptoms resembling dementia
Medical understanding of CTE is still developing. Currently, the only way to confirm that a person has CTE is for a doctor to diagnose them after death by inspecting the brain. However, if you have experienced repeated head injuries and are experiencing memory loss coupled with signs of impulsive behavior, aggression, and other behavioral problems, this can be a sign pointing to CTE.
What Should I Do After a Concussion?
Experiencing a traumatic brain injury should be followed by a medical evaluation. You are at grave risk of injuring your brain again before it has healed. You should make rest a priority. Any activity that will jostle or jar your head should be strictly avoided.
A Personal Injury Lawyer Can Help if You’re Dealing With Delayed Concussion Symptoms
If you’ve been experiencing delayed concussion symptoms because of another person’s negligence, a brain injury lawyer can assist you with filing a claim and seeking monetary compensation to treat concussion symptoms. A traumatic brain injury can take a toll on your finances and well-being. A skilled personal injury lawyer can evaluate whether you would be entitled to damages for medical bills, lost wages, and pain and suffering.
Contact Our Charleston Personal Injury Law Firm Today
If you were injured in an accident in Charleston, SC, and need legal help, contact our Charleston personal injury lawyer at Ty Robinson Personal Injury & Car Accident Law Firm to schedule a free case review today.
Ty Robinson Personal Injury & Car Accident Law Firm
28 Broad St Suite 204-2
Charleston, SC 29401
(843) 278-2222